Educational institutions are implementing different methods and techniques to enhance the teaching and learning process. One such framework used by teachers and students alike is the SOLO taxonomy.
What is SOLO taxonomy?
Structure of Observed Learning Outcomes (SOLO) taxonomy is a model for learning that helps describe or identify the understanding level of students in a subject. In layman’s terms, this framework is used for understanding or measuring a student’s depth of knowledge in a particular subject.
SOLO taxonomy is perceived to be a practical model because it helps in observing and measuring learning outcomes. Students and teachers use this framework. Want to know why? Read on.
Importance of SOLO taxonomy
- SOLO taxonomy is easy to use. Hence, students reflect on their level of understanding of a subject. Based on this, they could devise a strategy for enhancing their understanding.
- It could be used for different types of assignments and subjects.
- It helps teachers strategically develop learning materials to provide students a good learning experience.
- It helps teachers to develop learning outcomes and marking criteria for subjects and pointers for achieving the academic goal.
- It helps students recognise that the learning outcome results from strategies and effort, not static ability.
- Unlike its predecessor, Bloom’s taxonomy, SOLO taxonomy facilitates effective feedback.
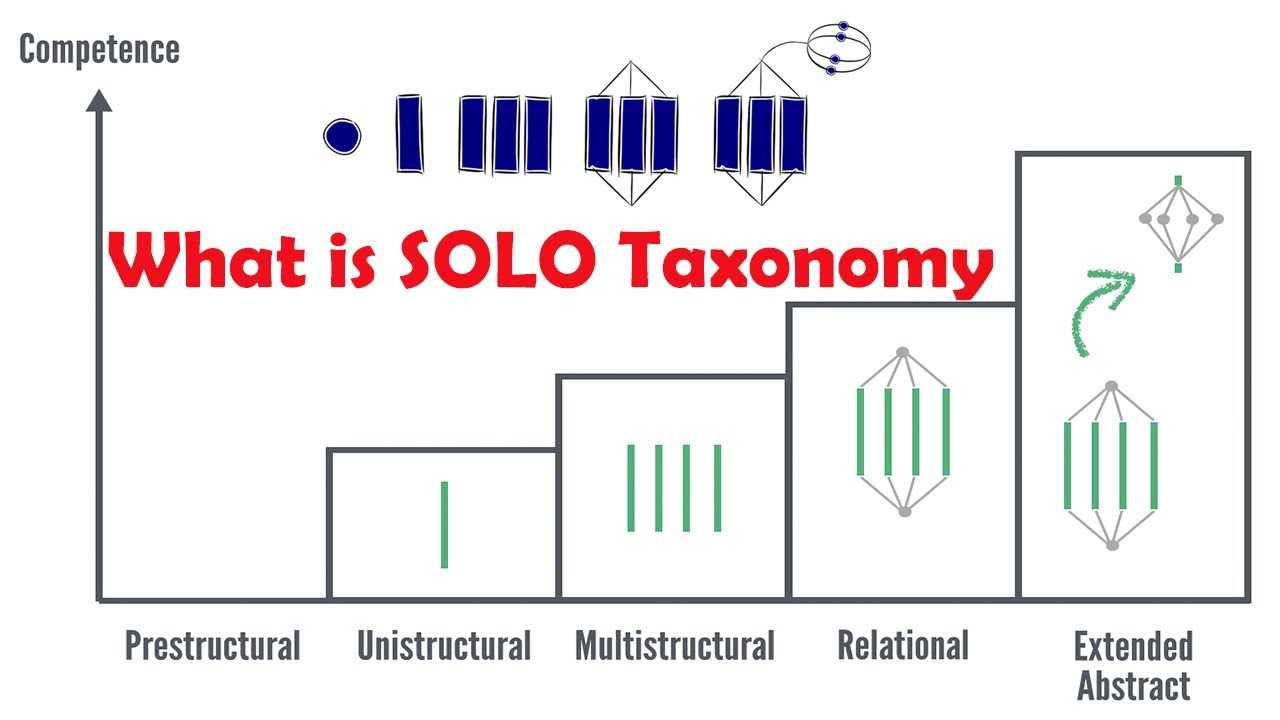
Level of SOLO taxonomy
SOLO taxonomy has five levels or hierarchies: pre-structuralural level, uni-structural level, multi-structural level, relational level and extended abstract level. The first 3 levels are associated with surface analysis and deductive reasoning. The last 2 levels are associated with topic understanding and knowledge depth.
- Pre-structural level: In this first level, the student has no knowledge about the topic and has no sufficient information. When students from this level are asked a question in a particular subject, their response would be more or less “I don’t know”, or they repeat what others have said or say something irrelevant.
- Unistructural level: In this level, the students acquire basic knowledge about a subject or some concepts from a subject. For example, they would know the terms or definition in a subject. However, they would not have entirely understood the subject.
- Multistructural level: In this level, the students acquire knowledge about different concepts in a subject. This is where the student would have developed a surface-level understanding. For example, they would memorise and remember the concepts. However, identifying the relationship between the learned concepts would be challenging for students at this level.
- Relational level: In this level, the students can identify the relationship between the different concepts. This helps them to have different perspectives on a topic from a subject.
- Extended abstract level: In this final level, the student’s knowledge and understanding of a subject are complete. They can practically apply the concepts in real life in different contexts.
The SOLO taxonomy framework helps enhance the knowledge level of the students. It helps both teachers and students. Hence, educational institutions should use this taxonomy.